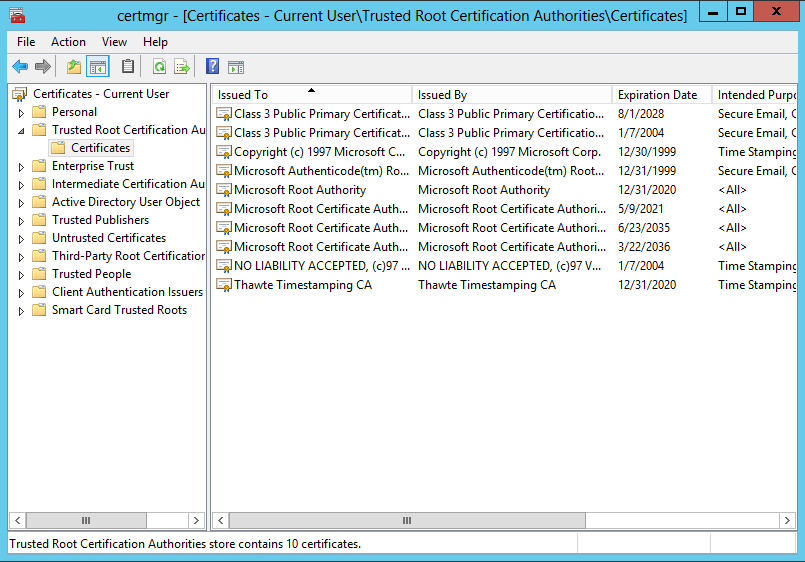
In today’s interconnected digital landscape, the security and integrity of communication often hinge on the proper management of digital certificates. These essential digital credentials authenticate identities, encrypt data, and ensure trust across networks and applications. Within an Active Directory Certificate Services (AD CS) environment, certificates are frequently issued based on certificate templates, which define their properties, uses, and issuance policies. The process to update certificates that use certificate templates is a critical aspect of maintaining a robust and secure infrastructure, ensuring that digital identities remain valid, secure, and compliant with current organizational policies and cryptographic standards.
Effective certificate lifecycle management extends far beyond initial issuance. Certificates have a finite lifespan, and their cryptographic strength must evolve to counter emerging threats. Furthermore, changes in organizational roles, user attributes, or application requirements can necessitate modifications to existing certificates. Understanding the various methods and best practices for updating these certificates is paramount for IT administrators and security professionals to prevent outages, security breaches, and non-compliance.
This comprehensive guide delves into the nuances of managing certificates that leverage templates, offering insights into why updates are necessary, the different approaches available, and crucial considerations for a seamless and secure transition. From automatic renewal mechanisms to manual re-enrollment, we will explore the technical steps and strategic thinking required.
Neglecting certificate updates can lead to significant operational disruptions. Expired certificates can halt critical services, block user access, and cause trust failures in secure communications. Therefore, a proactive and well-defined strategy for managing these updates is not just a best practice but a fundamental requirement for maintaining a resilient and secure computing environment.
Understanding Certificate Templates and Their Lifecycle
Certificate templates are the blueprints used by a Certificate Authority (CA) to issue certificates. They predefine properties such as the validity period, key usage, encryption algorithms, required subject information, and security permissions for enrollment. When a user, computer, or service requests a certificate, they typically do so based on a specific template. This standardization streamlines the certificate issuance process and ensures consistency across an organization.
The lifecycle of a certificate begins with issuance, followed by its active use, and eventually reaches expiration, revocation, or replacement. Throughout this lifecycle, there can be various reasons why a certificate might need to be updated. The most common reason is expiration, as all certificates are issued with a finite validity period. However, updates might also be driven by changes in security posture, such as a requirement for stronger cryptographic keys, or by operational necessities, like changes in an application’s subject alternative names (SANs). Understanding this lifecycle is the first step in mastering how to update certificates.
Beyond simple expiration, a certificate might need an update if its private key is suspected of being compromised, requiring immediate revocation and re-issuance. Policy changes within an organization can also dictate updates; for instance, if the acceptable key length for a particular certificate type increases, existing certificates using weaker keys would need to be re-issued to meet the new standard. This dynamic environment necessitates flexible and efficient methods for managing certificate updates.
Common Scenarios Requiring Certificate Updates
Numerous situations necessitate updating existing digital certificates. Recognizing these scenarios is crucial for proactive certificate management and preventing potential system outages or security vulnerabilities.
One of the most frequent reasons to update certificates is certificate expiration. Every certificate has a predefined validity period, after which it becomes invalid. Allowing certificates to expire can lead to service outages, failed authentications, and trust errors in applications relying on those certificates. Proactive renewal is essential to maintain continuous operation.
Another critical scenario involves changes in cryptographic requirements or best practices. As computing power advances, older cryptographic algorithms and key lengths can become vulnerable. Organizations might need to update certificates to use stronger algorithms (e.g., moving from SHA-1 to SHA-256 or RSA 2048 to RSA 4096) or more secure key types (e.g., from RSA to ECC) to maintain compliance and security posture. This often involves re-issuing certificates based on a modified or new template.
Policy changes within an organization can also trigger certificate updates. For example, if the required key usage for a specific application certificate changes, or if new extensions need to be included, existing certificates might no longer comply. Similarly, changes to naming conventions or subject alternative names (SANs) for services often require new certificates to be issued with the updated information.
Key compromise or suspected compromise is a severe scenario that demands immediate action. If there’s any indication that a certificate’s private key has been accessed by an unauthorized party, the certificate must be revoked and a new one issued. This is a critical security measure to prevent impersonation and unauthorized access.
Finally, application or service migration/upgrades can sometimes necessitate certificate updates. New versions of software or operating systems might have different certificate requirements or a need for certificates to be re-issued for compatibility or enhanced security features. Regular key rotation, even without a specific incident, is also a best practice to mitigate the risk of long-term key exposure.
Methods to Update Certificates That Use Certificate Templates
Updating certificates that use certificate templates can be achieved through various mechanisms, ranging from fully automated processes to manual interventions. The choice of method often depends on the certificate’s purpose, the environment’s configuration, and the specific reasons for the update.
Automatic Renewal/Auto-enrollment
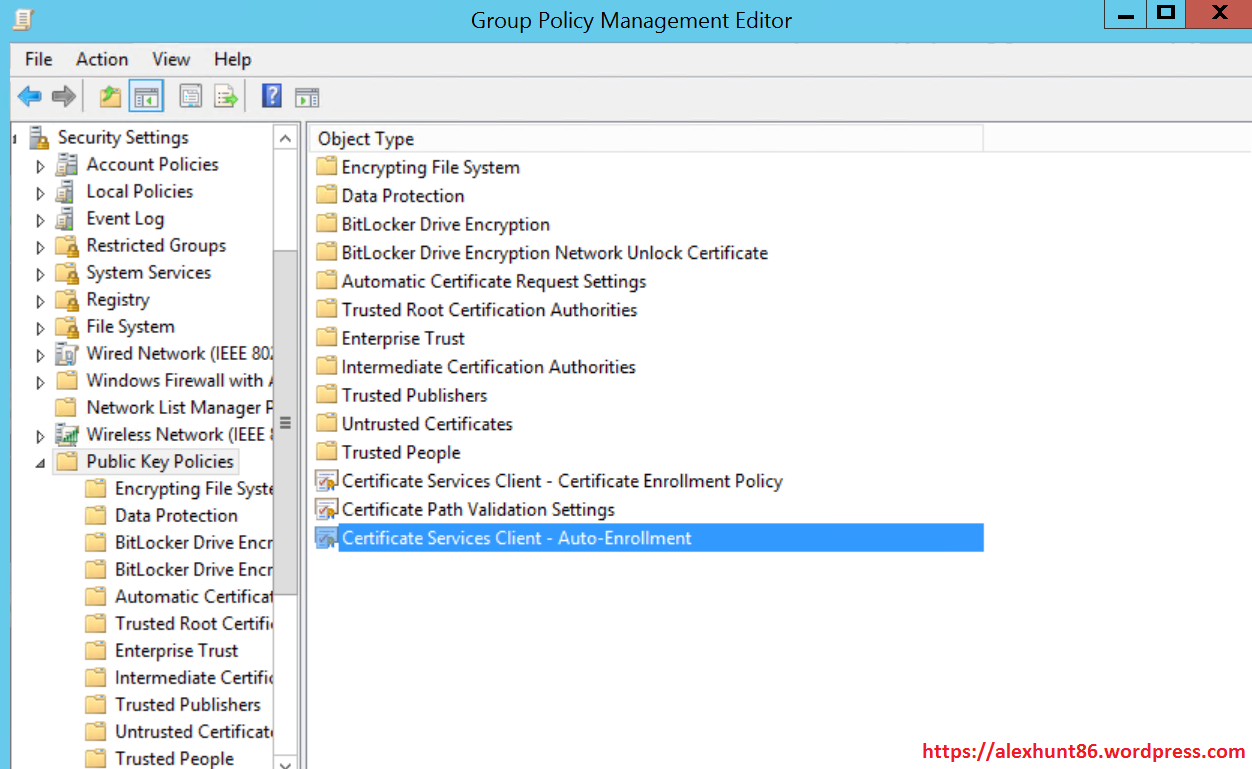
The most efficient and recommended method for managing certificate updates, especially for user and computer certificates, is automatic renewal through auto-enrollment. This feature, leveraging Group Policy in an Active Directory environment, allows clients to automatically request, renew, and install certificates from a CA without manual intervention.
To enable auto-enrollment, several prerequisites must be met:
* The Certificate Authority must be running AD CS.
* The client computers or users must be members of the Active Directory domain.
* A Group Policy Object (GPO) must be configured to enable auto-enrollment for users and/or computers. This GPO defines which certificate templates are eligible for auto-enrollment and the permissions required.
* The certificate templates themselves must be configured for auto-enrollment, specifically allowing “Enroll” and “AutoEnroll” permissions for the relevant security groups (e.g., Authenticated Users, Domain Computers).
When auto-enrollment is properly configured, clients will periodically check with the CA. If a certificate issued from an auto-enrollment-enabled template is nearing expiration (typically 6-8 weeks before, configurable within the template), or if the certificate template has been updated on the CA, the client will automatically request a new certificate. This new certificate is then seamlessly installed, often replacing the old one. This process significantly reduces the administrative overhead and minimizes the risk of service outages due to expired certificates.
Manual Renewal through MMC
While auto-enrollment is ideal, there are scenarios where manual renewal is necessary, such as for server certificates that require specific configurations, or when troubleshooting auto-enrollment failures. The Certificates snap-in in Microsoft Management Console (MMC) is the primary tool for manual certificate management.
To manually renew an existing certificate:
1. Open MMC and add the Certificates snap-in (for “My user account,” “Service account,” or “Computer account,” depending on the certificate holder).
2. Navigate to the appropriate certificate store (e.g., Personal -> Certificates).
3. Locate the certificate nearing expiration that needs to be renewed.
4. Right-click the certificate, select All Tasks, and then choose Renew Certificate with New Key… or Renew Certificate with Same Key…. Choosing “New Key” is generally more secure for key rotation.
5. Follow the wizard prompts. This process typically sends a renewal request to the CA, which then issues a new certificate based on the original template’s properties.
This method provides granular control but requires individual attention for each certificate, making it less scalable for large environments.
Re-enrollment (When Renewal Isn’t an Option)
Sometimes, simply renewing a certificate is not sufficient. If the underlying certificate template has undergone significant changes that fundamentally alter the certificate’s properties (e.g., a change in key type, extensions, or subject naming requirements), or if a certificate is revoked, a re-enrollment process is required. Re-enrollment effectively means requesting a completely new certificate, rather than just extending the validity of an existing one.
Re-enrollment is necessary when:
* The original certificate is revoked due to key compromise or policy violation.
* The certificate template has been modified in such a way that existing certificates no longer conform (e.g., new Subject Alternative Names (SANs) are needed, or a different key algorithm is required).
* A user or computer needs a certificate with different properties that are only available through a different template.
To re-enroll, you would typically follow a similar process to requesting a brand new certificate. This often involves:
1. Opening the Certificates snap-in in MMC.
2. Right-clicking the “Personal” (or appropriate) store, selecting All Tasks, then Request New Certificate….
3. Following the wizard, selecting the appropriate certificate enrollment policy and the desired template.
4. Completing the enrollment process, which generates a new private key and requests a new certificate from the CA.
This approach ensures that the new certificate fully incorporates any template changes or new requirements, effectively replacing the old, potentially non-compliant or compromised certificate.
Preparing Your Environment to Update Certificates That Use Certificate Templates Effectively
A well-prepared environment is key to successfully updating certificates and minimizing disruption. This involves more than just knowing how to click “renew”; it requires strategic planning and configuration management.
Reviewing Existing Certificate Templates
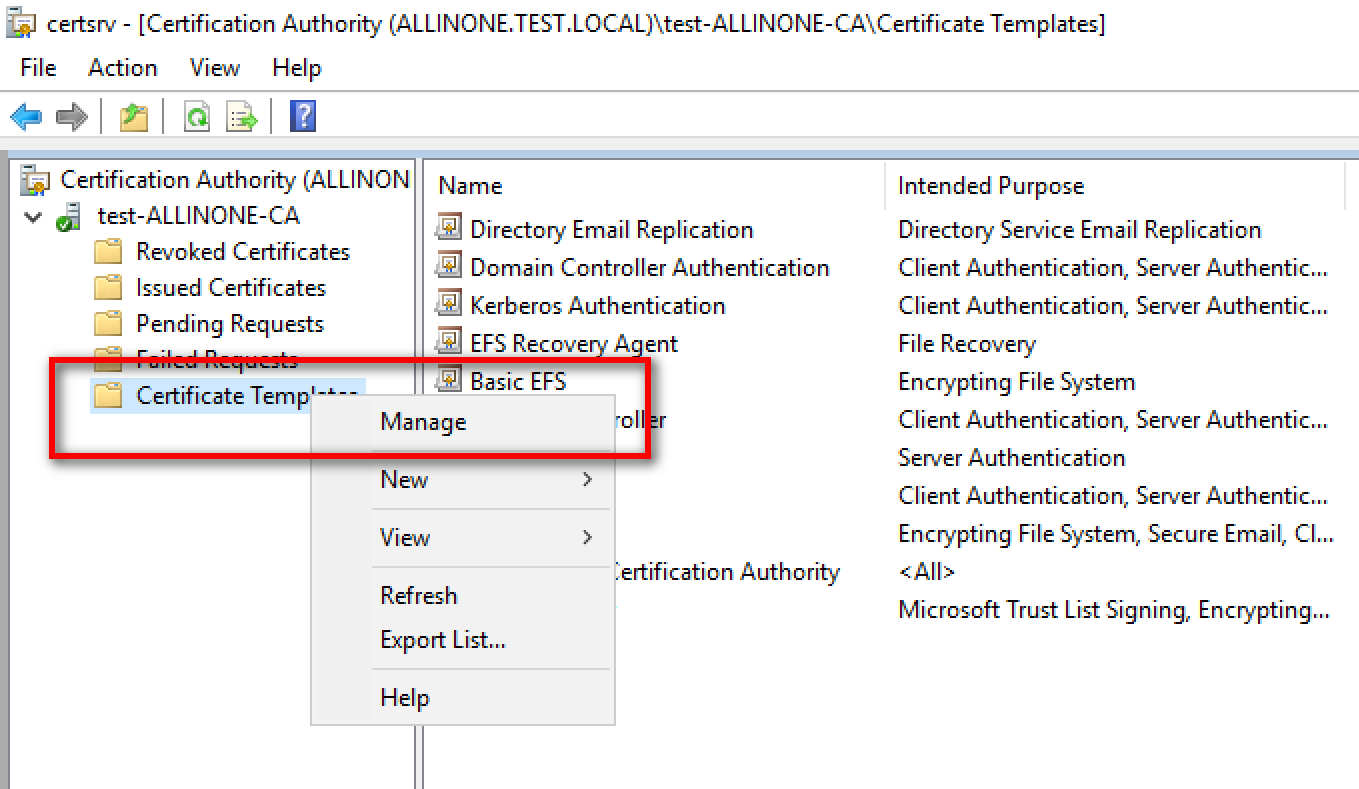
Before attempting to update certificates that use certificate templates, it’s crucial to review the current state of your certificate templates. This includes understanding their purpose, validity periods, key usage, security permissions, and cryptographic settings. Identify which templates are critical for your infrastructure and which certificates are issued from them. This inventory will inform your update strategy. Check the template versioning; significant changes in a template can necessitate re-enrollment rather than simple renewal.
Modifying Template Properties
If the reason for the update stems from policy changes (e.g., increased key length, new extensions, longer validity period), you’ll need to modify the certificate template itself. This is done through the Certificate Templates console on a CA administrator workstation.
When modifying a template:
* Duplicate the template first if you want to keep the old version or test changes. This is highly recommended for safety.
* Adjust properties like Validity period, Renewal period, Key Usage, Cryptographic Provider, Subject Name construction, and Extensions.
* Crucially, review the Security tab to ensure that the correct users and groups have “Enroll” and “AutoEnroll” permissions for the updated template.
* Increment the Template Version if making substantial changes that should trigger re-enrollment.
Issuing Updated Templates on the CA
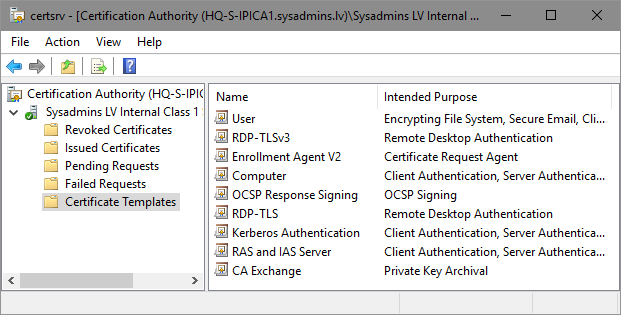
After modifying or creating a new certificate template, it must be issued on the Certificate Authority to make it available for enrollment. This is done through the Certification Authority console:
1. Open the Certification Authority console.
2. Right-click on Certificate Templates.
3. Select New -> Certificate Template to Issue.
4. Choose the updated or new template from the list and click OK.
Once issued, the CA will begin to process requests for certificates based on this template.
Group Policy Considerations for Propagation
For auto-enrollment to work, Group Policy plays a vital role. Ensure that the GPO linking and security filtering are correctly configured for the users and computers that need to update their certificates. After template modifications or issuance, Group Policy refresh intervals (or a gpupdate /force command) will ensure clients receive the updated policy and begin the auto-enrollment process if applicable. It’s often beneficial to test GPO propagation on a small set of clients before a wider rollout.
Testing the Update Process
Before a large-scale deployment, always test the certificate update process in a controlled test environment. This allows you to verify that certificates are renewing or re-enrolling as expected, applications are recognizing the new certificates, and no unexpected issues arise. Test both automatic and manual update scenarios relevant to your environment. This preventative measure can save significant headaches and downtime in a production environment.
Troubleshooting Common Certificate Update Issues
Despite careful planning, certificate update issues can arise. Understanding common problems and their solutions is vital for maintaining a smooth certificate lifecycle.
A frequent culprit is permissions problems. For auto-enrollment to succeed, the security principal (user or computer) must have “Read,” “Enroll,” and “AutoEnroll” permissions on the certificate template. Additionally, the CA must be configured to allow auto-enrollment, and the client needs network access to the CA. Incorrectly configured permissions on the template or within Active Directory are common reasons for enrollment failures.
Template misconfigurations can also lead to issues. This includes incorrect validity periods, missing extensions, or improper key usage settings that prevent a certificate from being issued or functioning correctly. For example, if a web server certificate template doesn’t allow “Server Authentication” key usage, the web server won’t be able to use it. Always double-check template settings against the certificate’s intended purpose.
Network connectivity to the CA is another basic but critical factor. Clients must be able to communicate with the CA and download the latest Certificate Revocation Lists (CRLs) and Authority Information Access (AIA) pointers. Firewall rules blocking port 135 (RPC Endpoint Mapper) or dynamic RPC ports, or issues with DNS resolution, can prevent clients from reaching the CA.
Expired intermediate CAs or problems with the certificate chain can also cause trust issues. If any certificate in the chain from the root CA to the issued certificate is expired, revoked, or untrusted, the entire chain breaks. Regularly audit your CA hierarchy for validity.
Client-side issues like a corrupted certificate store or problems with the local computer’s crypto API can sometimes prevent certificate updates. Clearing the certificate store or checking system event logs for cryptographic errors can help diagnose these rare occurrences. Using the certutil -store my command can help view certificates and identify issues.
Finally, Group Policy processing failures can prevent auto-enrollment settings from reaching clients. Use gpresult /r and gpupdate /force on client machines, and check event logs for GPO application errors. Ensuring that Group Policy is refreshing correctly is fundamental for automated certificate management.
Best Practices for Certificate Lifecycle Management
Effective certificate lifecycle management is a proactive discipline that underpins the security and operational continuity of any enterprise. Adhering to best practices can significantly reduce risk and administrative burden.
Implement a centralized certificate inventory and monitoring system. Manually tracking hundreds or thousands of certificates is unfeasible and error-prone. Tools for discovery, inventory, and expiration monitoring are essential. These systems can provide alerts well in advance of expiration, allowing ample time for renewal or re-enrollment. They also help identify certificates that are no longer needed or are misconfigured.
Automate certificate issuance and renewal wherever possible. Leveraging auto-enrollment via Group Policy is a prime example of this. For server and application certificates that cannot use auto-enrollment, consider using certificate management solutions that integrate with AD CS to automate request, issuance, and installation processes. Automation minimizes human error and ensures timely updates.
Implement strong key management policies. This includes requiring appropriate key lengths (e.g., RSA 2048 or 4096, or ECC P-256/P-384), enforcing key rotation, and protecting private keys. Avoid using the “Renew certificate with same key” option unless absolutely necessary, as rotating keys enhances security. Secure storage of private keys, especially for server certificates, is paramount.
Regularly review and update certificate templates. As security standards evolve, so too should your templates. Periodically assess your templates to ensure they align with current best practices for cryptography, key usage, and security permissions. Deprecate outdated templates and introduce new ones to reflect modern requirements. This helps maintain a robust and forward-looking PKI.
Establish clear roles and responsibilities for certificate management. Define who is responsible for creating/modifying templates, issuing certificates, monitoring expirations, and troubleshooting issues. Clear accountability helps streamline the process and prevents certificates from falling through the cracks.
Maintain a comprehensive recovery plan for your CA infrastructure. This includes regular backups of the CA database, private keys, and configuration. In the event of a CA failure, a robust recovery plan ensures that you can restore certificate services and continue issuing and updating certificates without significant downtime.
Educate users and administrators on certificate best practices. Awareness of certificate importance, proper handling, and common issues can significantly contribute to overall security and efficiency.
Conclusion
The ability to update certificates that use certificate templates is an indispensable skill for any IT professional managing an Active Directory Certificate Services environment. Certificates are the cornerstone of digital trust and security, and their timely and accurate management directly impacts an organization’s operational continuity and resilience against cyber threats. From understanding the core principles of certificate templates to mastering the various update methods, a holistic approach is required.
We have explored the critical reasons necessitating certificate updates, ranging from routine expiration to evolving cryptographic standards and security incident responses. The practical steps involved in automatic auto-enrollment, manual renewal via MMC, and the more comprehensive re-enrollment process provide a versatile toolkit for addressing diverse update scenarios. Crucially, preparing the environment by reviewing and modifying templates, issuing them correctly, and leveraging Group Policy ensures a smooth and effective update process.
Furthermore, a proactive stance on troubleshooting common issues and adhering to best practices—such as centralized inventory, automation, strong key management, and regular template reviews—elevates certificate management from a reactive chore to a strategic security function. By embracing these principles, organizations can ensure their digital identities remain robust, trusted, and fully compliant, safeguarding their data, communications, and operations in an ever-evolving digital landscape.
]]>