Navigating the complex landscape of cybersecurity requires meticulous attention to detail and a structured approach to identifying and mitigating risks. Organizations, regardless of size or industry, increasingly rely on security audits to assess their defenses, uncover vulnerabilities, and ensure compliance with ever-evolving regulatory frameworks. However, the true value of an audit often lies not just in its execution, but in the clarity and actionability of its findings. This is where a robust Security Audit Report Template becomes an indispensable tool, transforming raw data into a strategic roadmap for enhancing an organization’s security posture.
A well-crafted security audit report serves as the official record of an assessment, documenting everything from the scope of the audit to the specific vulnerabilities discovered and the recommended actions for remediation. Without a standardized format, these reports can become inconsistent, difficult to understand, and less effective in driving necessary security improvements. The sheer volume of information generated during an audit can be overwhelming, making structure and clarity paramount.
Implementing a consistent template ensures that all critical aspects of a security assessment are uniformly covered, making it easier for stakeholders to interpret findings and prioritize responses. It acts as a guide for auditors, ensuring no crucial detail is overlooked, and provides a clear narrative for decision-makers. From the executive summary that captures the high-level risks to the detailed technical findings and actionable recommendations, every section plays a vital role in communicating the organization’s security health.
Ultimately, the goal of any security audit is to reduce risk and protect valuable assets. A well-utilized template streamlines this process, fostering better communication, facilitating compliance, and enabling proactive security management. It bridges the gap between technical assessment and strategic business decisions, empowering organizations to make informed choices about their cybersecurity investments and initiatives.
What is a Security Audit Report Template?
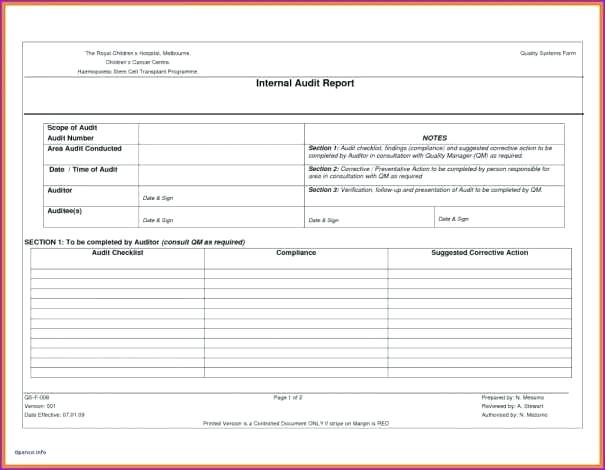
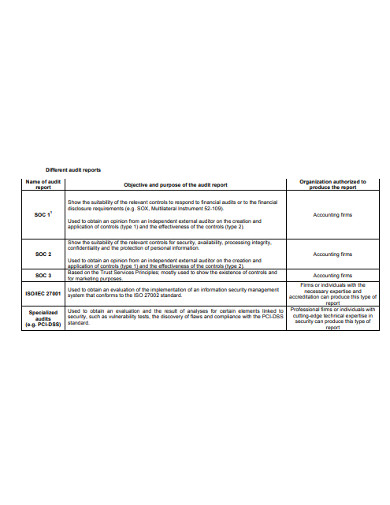
A Security Audit Report Template is a predefined, structured document designed to standardize the presentation of findings from a security audit. It provides a consistent framework for auditors to document their methodology, observations, identified vulnerabilities, risk assessments, and recommendations. This standardization is crucial for ensuring clarity, comparability, and completeness across different audits, whether they are performed internally or by third-party experts.
The primary purpose of such a template is to transform raw audit data into an easily digestible and actionable report for various audiences, from technical teams to executive management. It helps ensure that all critical elements of a security assessment are included, presented logically, and communicated effectively. Without a template, auditors might overlook important sections, present information inconsistently, or struggle to convey complex technical details in a business-relevant context.
Organized templates facilitate not only the reporting process but also the subsequent remediation efforts. By clearly categorizing findings and recommendations, they enable organizations to track progress on corrective actions, allocate resources efficiently, and demonstrate due diligence to auditors, regulators, and other stakeholders. In essence, a security audit report template is a blueprint for effective communication of cybersecurity posture and a catalyst for continuous improvement.
Key Components of an Effective Security Audit Report Template
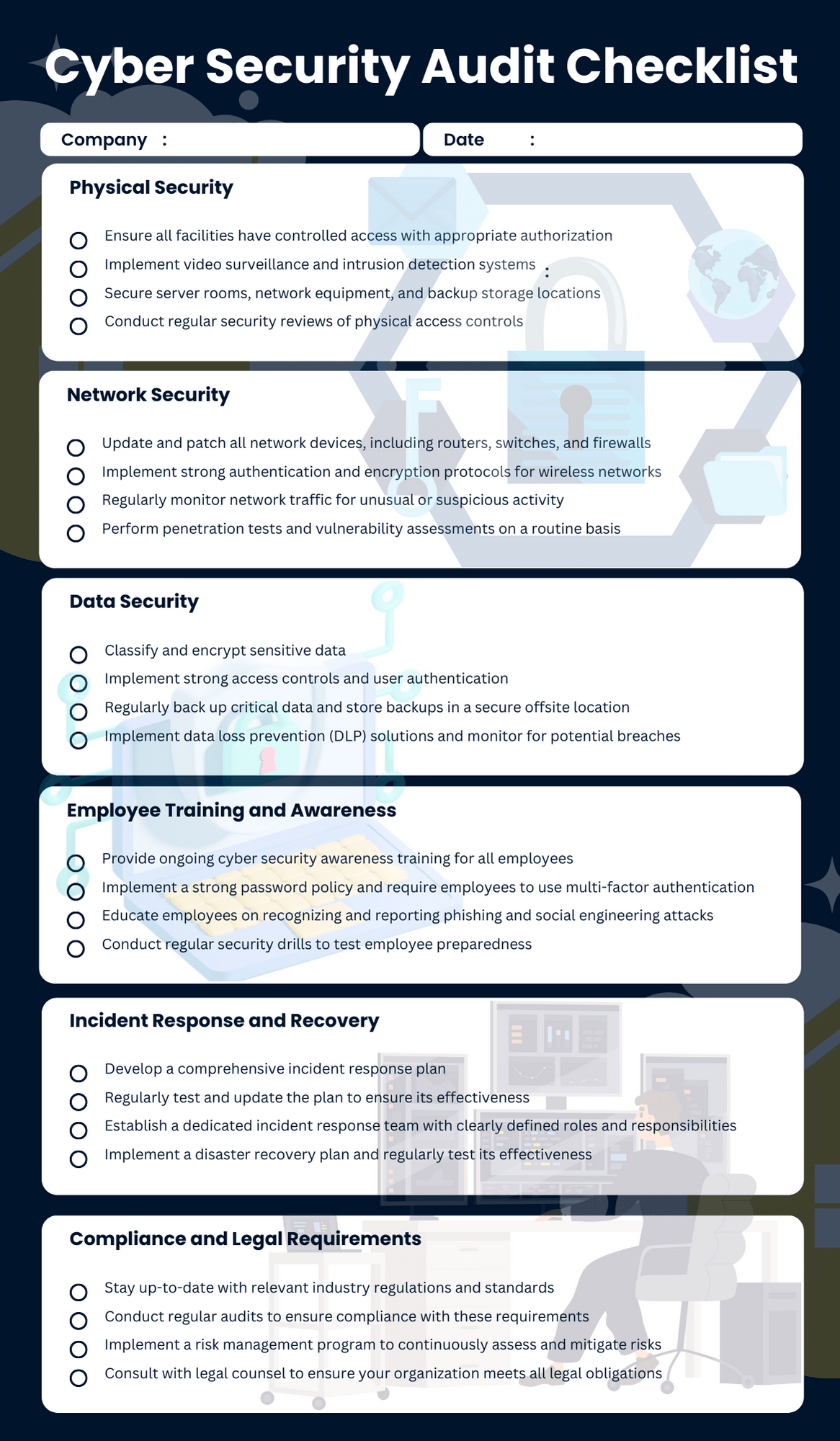
A comprehensive security audit report template should include several essential sections to ensure all pertinent information is captured and presented clearly. Each component serves a distinct purpose, contributing to the report’s overall effectiveness and utility.
Executive Summary
The Executive Summary is arguably the most critical section, designed for high-level stakeholders who need a quick, concise overview of the audit’s most important findings. It should summarize the audit’s scope, the key vulnerabilities discovered, their potential impact, and the highest-priority recommendations. This section should be non-technical, focusing on the business implications of the security posture, and typically concludes with an overall risk assessment or security rating.
Scope and Methodology
This section details what was audited (e.g., specific systems, networks, applications, policies) and how the audit was conducted. It outlines the objectives of the audit, the timeframe, the standards or frameworks used (e.g., NIST, ISO 27001, PCI DSS), and the tools and techniques employed (e.g., vulnerability scanning, penetration testing, configuration reviews, interviews). Clearly defining the scope and methodology provides context for the findings and establishes the audit’s credibility.
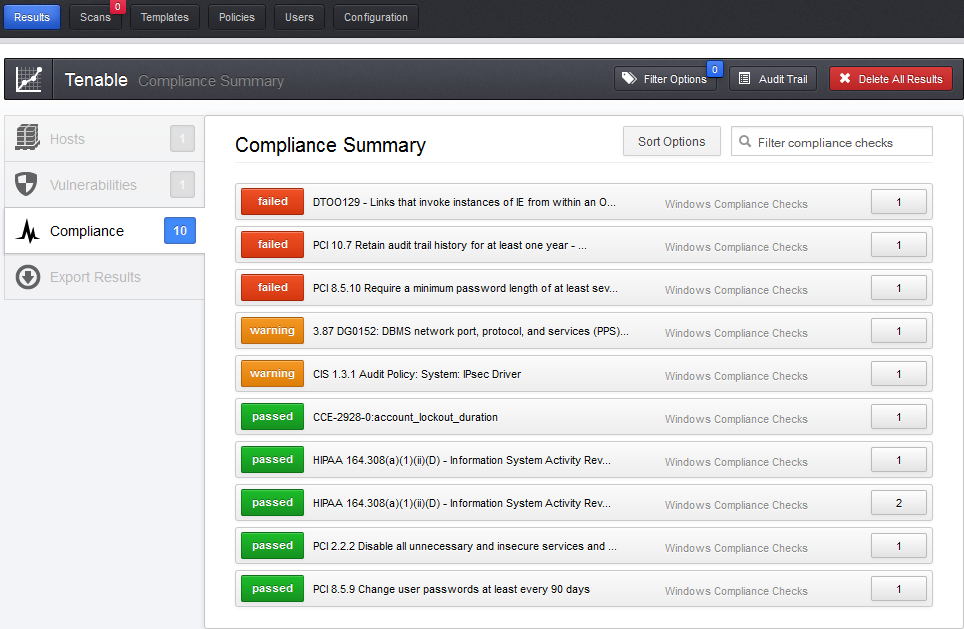
Findings and Observations
The Findings and Observations section is the core of the report, detailing every vulnerability, weakness, or non-compliance identified during the audit. Each finding should be presented clearly and consistently, typically including:
- Unique Identifier: For tracking purposes.
- Description: A clear, concise explanation of the vulnerability or issue.
- Affected Assets: The specific systems, applications, or processes where the finding was observed.
- Evidence: Screenshots, log entries, configuration excerpts, or other proof supporting the finding.
- Impact: The potential consequences if the vulnerability were exploited (e.g., data breach, service disruption, regulatory fines).
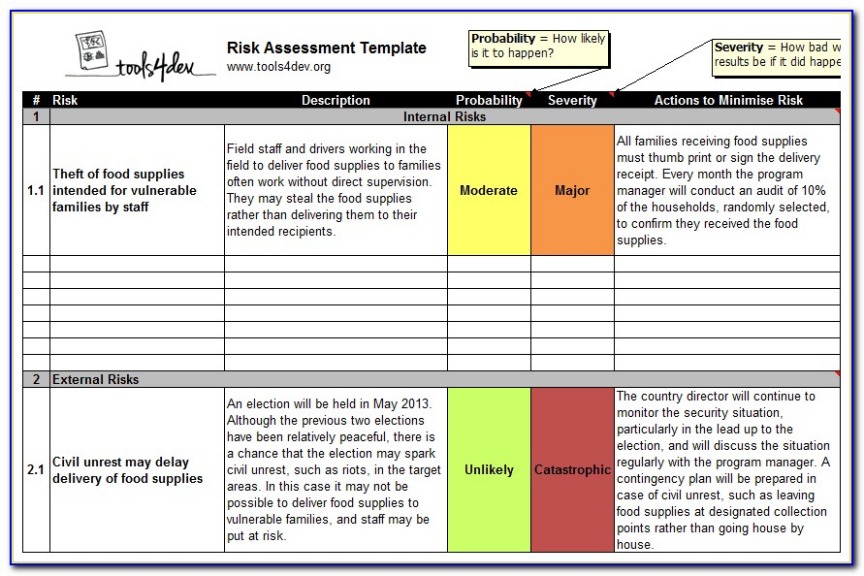
- Risk Rating: An assessment of the likelihood and impact, often using a standardized scale (e.g., Critical, High, Medium, Low).
Risk Assessment
Following the identification of findings, a dedicated Risk Assessment section synthesizes the individual risks into a broader understanding of the organization’s overall risk exposure. This section often includes a risk matrix or heat map, prioritizing findings based on their severity and likelihood. It helps stakeholders understand the aggregate impact of multiple vulnerabilities and guides decision-making on remediation.
Recommendations and Remediation Plan
For each finding, the report must provide actionable recommendations for remediation. These recommendations should be specific, practical, and prioritize solutions based on the associated risk level. This section often includes:
- Proposed Solution: Detailed steps to address the vulnerability.
- Estimated Effort/Resources: An indication of what might be required to implement the solution.
- Responsible Parties: Suggested teams or individuals for carrying out the remediation.
- Target Completion Date: A proposed timeline for addressing the issue.
Appendices
The Appendices section holds supplementary information that supports the main report but might be too detailed for the body. This can include:
- Detailed scan results
- Interview notes
- Configuration files
- Glossary of technical terms
- Relevant policies or procedures
- Legal disclaimers
Benefits of Using a Standardized Security Audit Report Template
Adopting a standardized Security Audit Report Template offers numerous advantages for both auditors and the audited organization, significantly enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of the security audit process.
Consistency and Clarity
A template ensures that all reports follow a uniform structure and language. This consistency makes reports easier to read, understand, and compare, regardless of who performed the audit or when it was conducted. It reduces ambiguity and provides a clear, consistent narrative of security posture over time.
Enhanced Efficiency
For auditors, templates streamline the reporting process by providing predefined sections and guidelines. This reduces the time spent on formatting and structuring, allowing auditors to focus more on the substantive findings and analysis. For the audited organization, a consistent format makes it quicker to locate critical information and prioritize remediation efforts.
Improved Communication
By standardizing the presentation of technical findings, a template helps bridge the communication gap between technical teams and non-technical stakeholders. The executive summary, for example, provides business leaders with the high-level insights they need without getting bogged down in jargon, while the detailed findings serve the technical teams.
Facilitates Compliance and Governance
Many regulatory frameworks and industry standards (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, ISO 27001) require clear documentation of security assessments and remediation activities. A well-structured report template helps organizations demonstrate due diligence and compliance, making it easier to satisfy audit requirements and respond to regulatory inquiries.
Better Decision-Making
With clear, consistent, and well-organized information, decision-makers are better equipped to understand the true state of their security, assess risks accurately, and allocate resources effectively for remediation and security improvements. The structured nature of the report helps in making data-driven decisions regarding cybersecurity investments.
Historical Tracking and Trend Analysis
Using a consistent template across multiple audits allows organizations to track their security posture over time. They can easily identify recurring vulnerabilities, measure the effectiveness of past remediation efforts, and observe trends in their overall security maturity. This historical data is invaluable for continuous improvement and strategic planning.
Creating Your Own Security Audit Report Template
While various generic templates are available, developing or customizing your own Security Audit Report Template is often beneficial to align it perfectly with your organization’s specific needs, industry, and compliance requirements.
Tailoring Your Security Audit Report Template to Specific Needs
No two organizations are exactly alike, and neither are their security audit needs. When creating or adapting a template, consider:
- Industry and Regulatory Requirements: If your organization operates in a regulated industry (e.g., healthcare, finance), ensure the template explicitly addresses relevant compliance frameworks (e.g., HIPAA, PCI DSS, GDPR).
- Organizational Structure: Adapt the language and level of detail to suit your internal reporting hierarchy. Some organizations might need highly technical reports, while others prefer more business-oriented summaries.
- Types of Audits: Differentiate templates for different types of audits, such as network penetration tests, web application security audits, compliance audits, or internal configuration reviews, as each may require specific sections.
- Maturity Level: As your organization’s security posture matures, your reporting needs might evolve. Your template should be flexible enough to accommodate more sophisticated analyses or metrics over time.
Integrating Industry Standards and Best Practices
Referencing established security standards and best practices can significantly enhance the quality and completeness of your template.
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework: Provides a comprehensive approach to managing cybersecurity risk. Incorporate its five functions (Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, Recover) into your risk assessment and recommendations.
- ISO 27001: An international standard for information security management systems. Ensure your template supports documenting controls and their effectiveness in alignment with ISO 27001 requirements.
- OWASP Top 10: For web application security audits, ensure your template facilitates reporting findings related to these common vulnerabilities.
- MITRE ATT&CK Framework: Can be used to categorize and describe attack techniques, providing a more detailed understanding of potential threats.
- Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS): Adopt CVSS for consistent and standardized risk scoring of vulnerabilities, providing a universally understood metric.
Utilizing Tools and Software
Modern cybersecurity tools and audit management platforms can often generate reports that can be integrated into or adapted for your template. Some platforms even offer customizable templates. Leveraging these tools can automate data collection, streamline risk scoring, and integrate with remediation tracking systems, further enhancing efficiency. Ensure your template is compatible with the output formats of your preferred security tools.
Best Practices for Writing an Effective Security Audit Report
Even with the best Security Audit Report Template, the quality of the report ultimately depends on how it’s written. Adhering to best practices ensures the report is impactful, actionable, and understood by its intended audience.
Know Your Audience
A security audit report typically has multiple audiences: executives, technical teams, legal counsel, and sometimes external auditors or regulators. Tailor the language and level of detail for each section. The executive summary should be concise and business-focused, while technical findings require sufficient detail for remediation teams. Avoid overly technical jargon without clear explanations.
Be Clear, Concise, and Objective
Write in plain language. Avoid vague statements or assumptions. Every finding should be supported by clear evidence. Be objective in your descriptions of vulnerabilities and their impact, avoiding sensationalism. The report should present facts, not opinions, allowing the data to speak for itself.
Provide Actionable Recommendations
It’s not enough to just identify problems; the report must offer practical and specific solutions. Recommendations should be clear, prioritized, and include sufficient detail for the responsible teams to implement them. Where possible, suggest specific configuration changes, software updates, or policy revisions.
Prioritize Findings with a Consistent Risk Rating
Utilize a standardized risk rating system (e.g., Critical, High, Medium, Low, or CVSS scores) for all findings. This allows the organization to quickly understand the most significant risks and prioritize remediation efforts effectively. Ensure the methodology for assigning risk ratings is clearly explained in the report.
Include Evidence and Context
Support every finding with verifiable evidence, such as screenshots, log excerpts, command outputs, or policy references. This not only validates the finding but also helps the remediation team understand the issue more quickly. Provide context for each vulnerability, explaining why it’s a risk and what its potential impact could be.
Maintain a Professional Tone
The report should always maintain a professional, respectful, and constructive tone. The goal is to identify and address security weaknesses, not to assign blame. Focus on solutions and improvements.
Review and Edit Thoroughly
Before finalization, rigorously review the entire report for accuracy, completeness, clarity, and grammatical errors. Ensure all sections are consistent and that the narrative flows logically. A well-edited report reflects professionalism and enhances credibility.
Common Challenges in Using a Security Audit Report Template and How to Overcome Them
While a Security Audit Report Template offers significant advantages, organizations may encounter challenges in its implementation and use. Addressing these proactively can maximize its effectiveness.
Lack of Customization
A common issue is using a generic template without adapting it to the organization’s unique environment, industry, or compliance needs. This can lead to irrelevant sections, missing critical information, or a report that doesn’t resonate with internal stakeholders.
- Solution: Invest time in customizing the template. Conduct a needs assessment to identify specific regulatory requirements, internal policies, and stakeholder expectations. Regularly review and update the template as your organization’s security posture and external landscape evolve.
Overwhelming Technical Detail
Reports can sometimes be overly technical, making it difficult for non-technical leadership to grasp the key risks and their business implications. Conversely, a lack of technical detail can hinder remediation teams.
- Solution: Ensure a clear separation between the executive summary (business-focused) and the detailed technical findings. Use clear, simple language in the summary. For technical sections, provide sufficient detail and evidence, and consider including a glossary of terms for clarity.
Inconsistent Risk Prioritization
Without a standardized approach, different auditors or teams might assign varying risk levels to similar vulnerabilities, leading to confusion and inefficient remediation efforts.
- Solution: Establish a clear, documented risk assessment methodology (e.g., based on CVSS, an internal risk matrix) that is consistently applied across all audits. Train all auditors on this methodology and include it in the report’s “Scope and Methodology” section.
Insufficient Actionable Recommendations
A report that merely lists vulnerabilities without providing clear, actionable steps for remediation is of limited value.
- Solution: For every finding, demand specific, practical, and prioritized recommendations. Auditors should consider the organization’s resources and capabilities when proposing solutions. Recommendations should include estimated effort, potential responsible parties, and a suggested timeline.
Resistance to Change
Implementing a new template or standardizing reporting processes can face resistance from auditors accustomed to their own methods or from teams who find the new structure burdensome.
- Solution: Communicate the benefits of standardization clearly to all stakeholders. Provide training and support. Start with a pilot program or phased implementation to gather feedback and make adjustments. Emphasize how the template will ultimately save time and improve overall security outcomes.
Conclusion
The journey towards a robust cybersecurity posture is continuous, and the Security Audit Report Template stands as a pivotal tool in this ongoing endeavor. Far more than just a document, it is a framework that brings structure, clarity, and actionability to the complex process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating security risks. By standardizing the communication of audit findings, it empowers organizations to make informed, data-driven decisions that directly enhance their defense mechanisms.
From ensuring consistent reporting across various assessments to facilitating compliance with critical regulations and fostering better communication between technical teams and executive leadership, a well-implemented template offers undeniable benefits. It transforms raw technical data into a strategic asset, providing a clear roadmap for remediation and continuous improvement. While challenges in customization or inconsistent application may arise, proactive measures and a commitment to best practices can overcome these hurdles, unlocking the full potential of structured security reporting. Ultimately, a diligently utilized security audit report template is not just about documenting problems; it’s about building a more resilient and secure future for any organization.
]]>