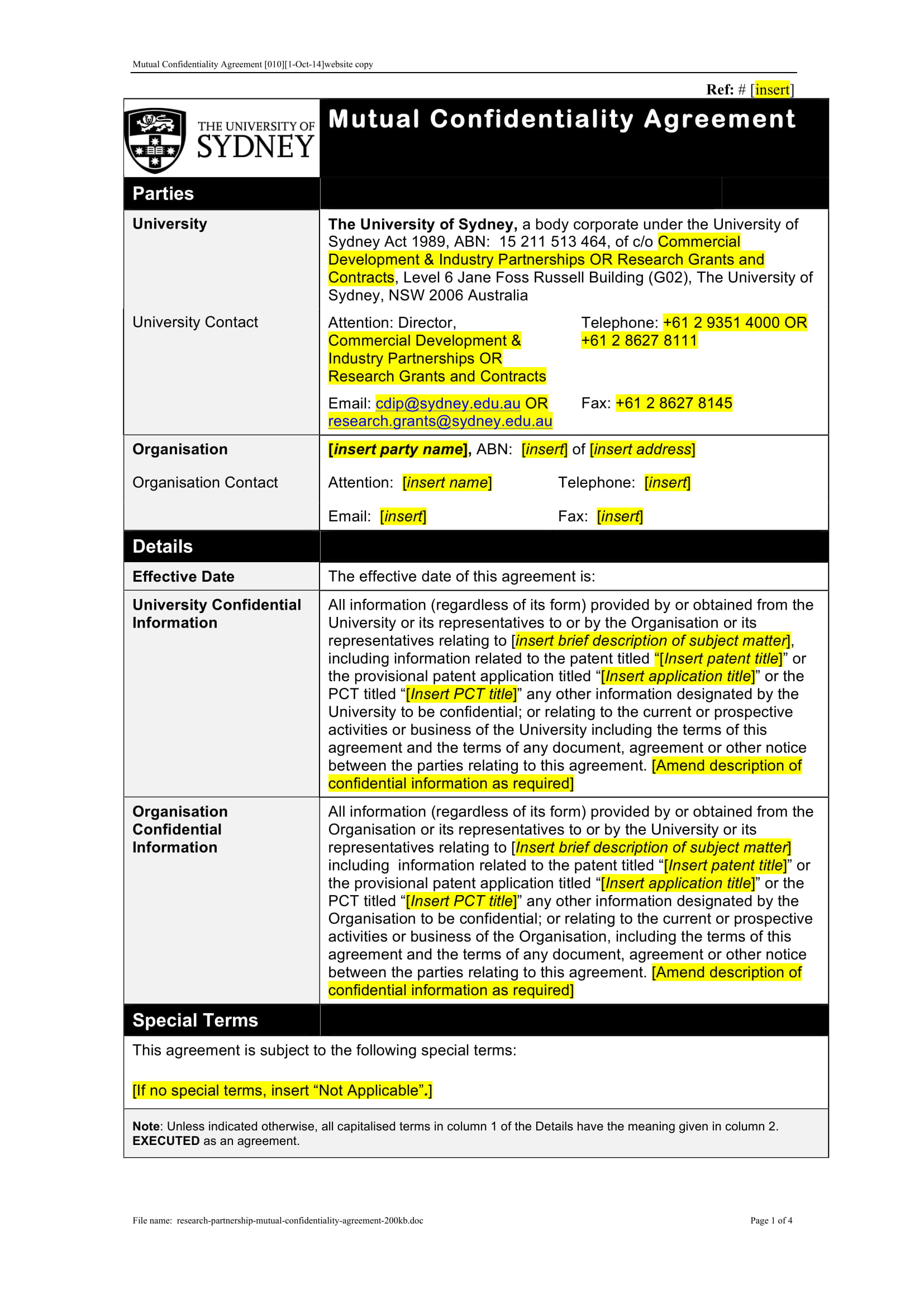
The world of business is increasingly reliant on data and information. Protecting sensitive client information and proprietary secrets is paramount, and a well-drafted Mutual Confidentiality Agreement (MCA) is a crucial safeguard. This article provides a comprehensive guide to creating and understanding a Mutual Confidentiality Agreement, ensuring both parties understand their obligations and protect their interests. A robust MCA minimizes legal risks and fosters trust within business relationships. It’s more than just a legal document; it’s a foundational agreement that sets the stage for a successful and mutually beneficial partnership. Understanding the nuances of an MCA is essential for any organization that handles confidential data. This template offers a starting point, and it’s always advisable to consult with legal counsel to tailor the agreement to your specific needs. Let’s delve into the key components and best practices for crafting a truly effective MCA.
Understanding the Importance of a Mutual Confidentiality Agreement
Before we dive into the specifics, it’s vital to grasp why an MCA is so important. In today’s digital landscape, data breaches and leaks are increasingly common. A poorly drafted MCA can leave a company vulnerable to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal action. Conversely, a well-structured MCA demonstrates a commitment to protecting sensitive information, building trust with clients, and safeguarding intellectual property. It’s a proactive measure that can prevent costly disputes and maintain a positive business relationship. The benefits extend beyond simply avoiding lawsuits; a strong MCA fosters a culture of respect and responsibility within the organization. It’s an investment in long-term success.
Defining the Scope of Confidentiality
The core of any MCA lies in clearly defining the scope of confidentiality. This section should explicitly state what information is considered confidential and what actions are prohibited. It’s crucial to be specific – avoid vague language. For example, instead of saying “all company information,” specify “customer lists, financial data, marketing strategies, and product designs.” The agreement should also outline the types of data that are considered confidential, including but not limited to trade secrets, client lists, pricing information, and internal processes. Consider including examples of what constitutes confidential information to avoid ambiguity. A clear definition of what is not considered confidential is equally important – this helps prevent misunderstandings and potential disputes. Failure to clearly define the scope can lead to disputes over what information is protected.
Key Clauses to Include in a Mutual Confidentiality Agreement
Several key clauses are typically included in an MCA. These include:
- Definition of Confidential Information: As mentioned above, a precise definition is critical.
- Permitted Uses: Specifies how the receiving party can use the confidential information. Restrictions on use are vital.
- Obligations of the Receiving Party: Details what the receiving party must do to protect the information.
- Term and Termination: Establishes the duration of the agreement and the conditions for termination.
- Data Security Measures: Requires the receiving party to implement reasonable security measures to protect the information.
- Return or Destruction of Information: Specifies how confidential information should be returned or destroyed upon termination of the agreement.
- Non-Disclosure: A clear statement that the receiving party will not disclose the information to any third party.
Protecting Against Unauthorized Disclosure
Unauthorized disclosure of confidential information is a major concern. The MCA should include provisions designed to deter and punish such breaches. This might include clauses requiring the receiving party to report any suspected breaches to the disclosing party immediately. It may also include provisions for injunctive relief, allowing the disclosing party to seek court orders to prevent further disclosure. Consider including a clause requiring the receiving party to implement a data breach response plan. A proactive approach to data security is essential for mitigating the risk of unauthorized disclosure.
Data Security and Access Controls
Implementing robust data security measures is a critical component of any MCA. The agreement should outline the security measures the receiving party is required to implement, including technical safeguards (e.g., encryption, firewalls) and administrative controls (e.g., access controls, employee training). It’s important to specify the level of access the receiving party is granted to the confidential information. Consider including provisions for regular security audits and vulnerability assessments. The MCA should also address data retention policies, specifying how long the receiving party is permitted to retain the confidential information.
Governing Law and Dispute Resolution
Clearly defining the governing law and dispute resolution mechanism is essential. This ensures that any disagreements will be resolved according to established legal principles. Commonly, the agreement will specify a jurisdiction (e.g., the state where the company is located) and a method for resolving disputes, such as mediation or arbitration. Mediation is often preferred as it can be less expensive and time-consuming than litigation. A well-defined dispute resolution process can help prevent costly and protracted legal battles.
Employee Responsibilities
The MCA should address the responsibilities of employees who have access to confidential information. It may include provisions requiring employees to sign a confidentiality agreement, which is a legally binding agreement that further protects the company’s interests. The agreement should also outline the consequences of violating confidentiality obligations.
The Role of Legal Counsel
While a well-drafted MCA can be created with reasonable effort, it’s often beneficial to seek legal counsel. A lawyer specializing in intellectual property and data privacy can ensure that the agreement is legally sound and tailored to your specific circumstances. They can also advise you on the applicable laws and regulations and help you navigate the complexities of data protection. A lawyer can also help you draft the agreement to ensure it complies with relevant privacy laws and regulations, such as GDPR or CCPA.
Benefits of a Comprehensive MCA
Implementing a comprehensive Mutual Confidentiality Agreement provides numerous benefits. It strengthens your company’s position in protecting sensitive information, fostering trust with clients, and mitigating legal risks. It also demonstrates a commitment to responsible data handling, which can enhance your reputation and build long-term relationships. Ultimately, a well-crafted MCA is an investment in the future of your business.
Conclusion
Creating a Mutual Confidentiality Agreement is a critical step in protecting your company’s valuable information. By carefully considering the scope of confidentiality, including key clauses, and seeking legal counsel, you can ensure that your agreement is robust, legally sound, and effectively protects your interests. Remember that a proactive approach to data security and a commitment to responsible data handling are essential for maintaining a competitive advantage in today’s digital world. Don’t underestimate the importance of this agreement – it’s a cornerstone of a successful and sustainable business relationship. Investing in a strong MCA is an investment in the long-term health and prosperity of your organization.