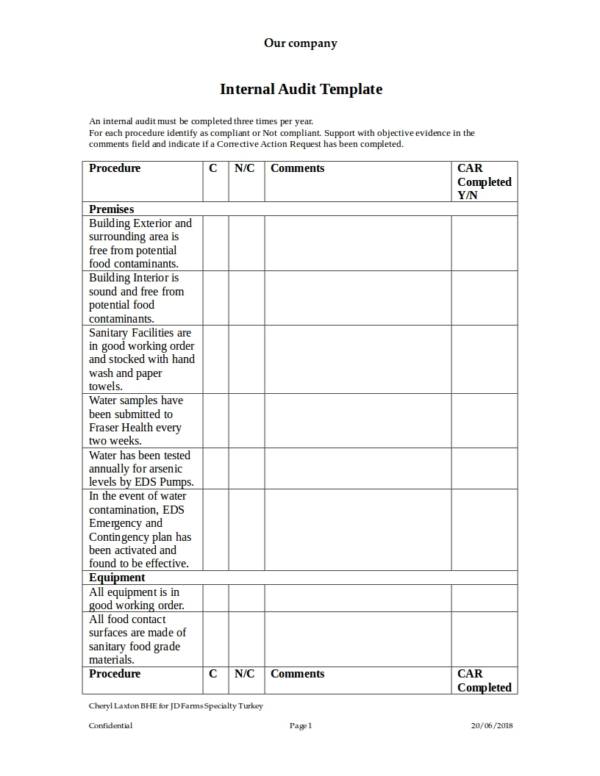
Data centers are the pulsating heart of modern business, housing critical infrastructure that underpins everything from daily operations to global digital economies. Ensuring their optimal performance, security, and compliance is not merely good practice, but an absolute imperative. A systematic approach to evaluating these complex environments is crucial, and central to this is a robust Data Center Audit Report Template. This indispensable tool provides a structured framework for documenting findings, identifying vulnerabilities, and formulating actionable recommendations, transforming raw audit data into clear, digestible insights for stakeholders.
Without a standardized template, data center audits can devolve into unorganized checklists and disparate notes, making comparisons across time or between different facilities nearly impossible. The lack of uniformity hinders effective decision-making and can obscure critical issues that demand immediate attention. A well-designed template streamlines the entire audit process, ensuring consistency, comprehensiveness, and clarity, which are vital for maintaining the integrity and resilience of your most valuable digital assets.
Implementing such a template not only formalizes the auditing process but also elevates its strategic value. It allows organizations to track improvements over time, demonstrate due diligence to regulators and clients, and proactively address potential risks before they escalate into costly disruptions. From physical security to network performance and environmental controls, every aspect of the data center operation can be meticulously examined and reported upon, creating a holistic view of its health and efficiency.
The structured nature of an audit report template facilitates effective communication among technical teams, management, and compliance officers. It distills complex technical information into understandable formats, enabling informed discussions and strategic planning. Ultimately, leveraging a comprehensive template empowers organizations to maintain superior operational standards, enhance security postures, and ensure continuous service delivery, thereby safeguarding their digital future.
Understanding the Importance of Data Center Audits
Data center audits are rigorous examinations designed to assess the performance, security, and efficiency of a data center’s infrastructure, operations, and policies. These audits are not just about finding flaws; they are about validating compliance, identifying areas for improvement, and mitigating potential risks that could lead to downtime, data breaches, or operational inefficiencies. The stakes are incredibly high, as the failure of a data center can halt business operations, damage reputation, and incur significant financial losses.
The criticality of regular audits stems from several factors. Firstly, the dynamic nature of technology means that data center environments are constantly evolving. New threats emerge, hardware ages, and software requires updates. Audits provide a snapshot of the current state, ensuring that the infrastructure remains aligned with business needs and industry best practices. Secondly, regulatory compliance is a non-negotiable aspect of many industries. Standards like HIPAA, PCI DSS, GDPR, and ISO 27001 demand stringent controls and documented evidence, which audits provide. Finally, audits are fundamental to maintaining operational excellence. They help identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies in power consumption, cooling issues, and suboptimal network configurations, all of which impact the bottom line and service quality.
Neglecting regular data center audits carries substantial risks. Unidentified vulnerabilities in physical security could lead to unauthorized access. Unaddressed environmental control issues could result in equipment failure due to overheating or power fluctuations. Outdated network configurations could create security loopholes or performance bottlenecks. Furthermore, without a clear record of an audit, demonstrating due diligence to stakeholders, insurers, or regulatory bodies becomes challenging, potentially leading to fines or legal repercussions in the event of an incident. A well-executed audit, underpinned by a robust reporting framework, is therefore a proactive measure that underpins business continuity and resilience.
Key Components of an Effective Data Center Audit
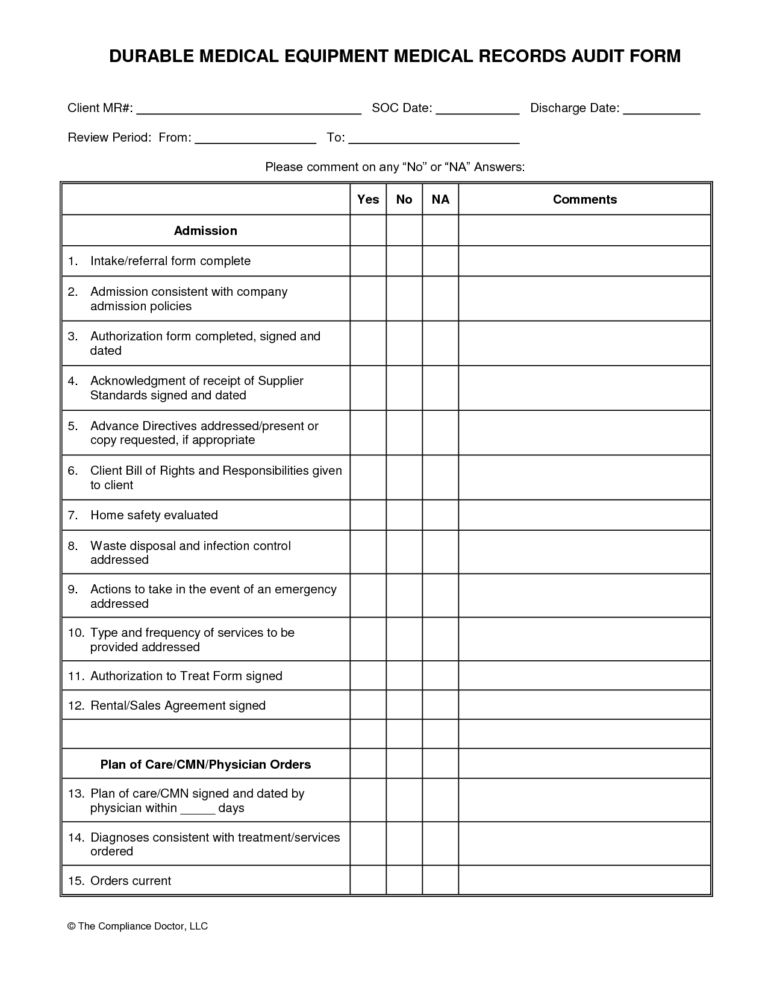
A comprehensive data center audit delves into multiple facets of the facility, each critical for overall functionality and security. To ensure nothing is overlooked, the audit typically covers a broad spectrum of areas, from the physical structure to the logical security layers and operational processes.
Physical Security Measures
Physical security is the first line of defense. Auditors examine entry points, surveillance systems (CCTV), access control mechanisms (biometrics, card readers), perimeter security, and visitor logging procedures. The presence of security personnel, their training, and response protocols are also evaluated. Effective physical security prevents unauthorized access to sensitive equipment and data.
Environmental Controls and Infrastructure
This section focuses on the non-IT infrastructure that keeps the IT equipment running smoothly. It includes the HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems, power infrastructure (UPS, generators, power distribution units), fire suppression systems, and water detection. Auditors assess the redundancy of these systems, their maintenance schedules, and their ability to handle peak loads. Proper environmental control is paramount to prevent equipment damage and ensure continuous operation.
Network Infrastructure Assessment
The network is the backbone of data communication. An audit will scrutinize network topology, device configurations (routers, switches, firewalls), cabling management, and network performance. It also covers network security protocols, intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS/IPS), and segmentation strategies. The goal is to ensure a secure, reliable, and high-performing network that supports business operations.
Server and Storage Infrastructure Review
This component involves evaluating the health, performance, and security of servers and storage devices. Auditors examine server utilization, patch management status, operating system configurations, and virtualization environments. For storage, they assess capacity, performance, data backup and recovery procedures, and data deduplication strategies. The focus here is on data integrity, availability, and efficient resource utilization.
Data Security and Compliance
This is arguably one of the most critical areas, covering logical security controls, data encryption, access management (identity and access management – IAM), and compliance with relevant regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, ISO 27001). Auditors verify security policies, incident response plans, vulnerability management, and penetration testing results. This section ensures that data is protected from breaches and meets legal and industry-specific mandates.
Operational Procedures and Documentation
An audit isn’t just about hardware and software; it’s also about the processes that govern their use. This includes change management procedures, incident management, asset management, maintenance logs, and operational staff training. Well-defined and documented procedures ensure consistent operation, reduce human error, and facilitate quick recovery from incidents.
Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
Auditors assess the organization’s ability to recover from disruptive events. This involves reviewing disaster recovery plans (DRP), business continuity plans (BCP), backup strategies, recovery time objectives (RTOs), and recovery point objectives (RPOs). Regular testing of these plans is crucial, and the audit verifies that such tests are conducted and documented effectively.
Structuring Your Data Center Audit Report Template
A well-structured Data Center Audit Report Template is the linchpin for transforming raw audit data into actionable insights. It provides a logical flow, ensuring all critical information is presented clearly and concisely, enabling stakeholders to quickly grasp the audit’s scope, findings, and recommendations. The report should tell a story, moving from a high-level summary to detailed technical observations and concluding with a strategic roadmap for improvement.
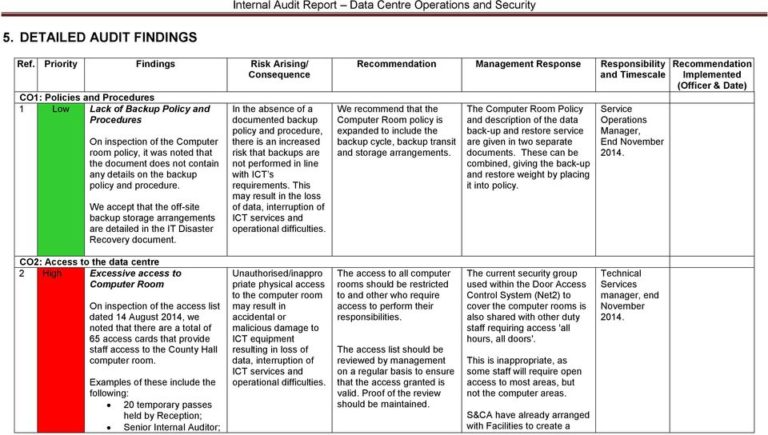
The template should typically begin with an Executive Summary, offering a distilled overview for senior management who may not delve into every technical detail. This is followed by a clear articulation of the audit’s scope and methodology, establishing the parameters of the review. The core of the report lies in its Findings section, where observations, vulnerabilities, and non-compliance issues are meticulously documented. Each finding should be supported by evidence and assigned a severity level. Crucially, the report must include concrete Recommendations, providing specific, actionable steps to address each identified issue, often accompanied by estimated timelines and responsible parties.
The format and presentation are key to the report’s effectiveness. Utilize clear headings (###), bullet points, and tables to break down information and improve readability. Visual aids such as charts or diagrams can be employed to illustrate complex data, such as power consumption trends or network topology. Consistency in terminology and formatting throughout the template is essential for professionalism and ease of understanding. A well-designed template ensures that the report serves not just as a record of findings, but as a strategic document guiding future data center improvements.
Detailed Sections within a Data Center Audit Report Template
To provide a truly comprehensive overview, a Data Center Audit Report Template should be meticulously divided into distinct sections, each serving a specific purpose in conveying the audit’s findings and recommendations.
Executive Summary: High-Level Insights
This section provides a concise overview of the entire audit for senior management and non-technical stakeholders. It should summarize the audit’s purpose, key findings (highlighting the most critical vulnerabilities), and the most impactful recommendations. The executive summary should be no more than one to two pages and written in non-technical language, focusing on business impact and strategic implications.
Audit Scope and Methodology
This section clearly defines what was included in the audit (e.g., specific data centers, departments, systems, or compliance standards) and what was explicitly excluded. It also details the methodology employed, such as interview processes, documentation reviews, physical inspections, tools used (e.g., vulnerability scanners), and the period covered by the audit. This establishes the context and boundaries for the report.
Findings: Physical Infrastructure
This part of the report documents observations related to the data center’s physical environment. It includes findings on building security (access controls, surveillance), environmental controls (HVAC, cooling efficiency, temperature/humidity monitoring), power infrastructure (UPS, generators, PDUs, grounding, capacity), and fire suppression systems. Each finding should include a description, evidence (e.g., photos, logs), the potential impact, and a severity rating (e.g., Critical, High, Medium, Low).
Findings: Logical and Operational Security
This section focuses on digital and procedural security. It covers findings related to network security (firewall rules, IDS/IPS effectiveness, network segmentation), server and application security (patch management, access controls, hardening), data security (encryption, backup integrity), and identity and access management. Operational security aspects such as change management, incident response, and asset management processes are also detailed here, along with their associated evidence, impact, and severity.
Findings: Compliance and Governance
Here, the report addresses the data center’s adherence to relevant regulatory requirements (e.g., PCI DSS, HIPAA, GDPR), industry standards (e.g., ISO 27001), and internal company policies. It highlights any areas of non-compliance, citing specific regulations or policies that are not being met. This section is crucial for organizations operating in regulated environments and demonstrates due diligence.
Recommendations and Action Plan
This is a critical section that translates findings into concrete steps. For each significant finding, a specific, actionable recommendation should be provided. These recommendations should include details on what needs to be done, how it should be done, and who is responsible. It’s often beneficial to include an estimated timeframe for completion and a priority level (e.g., Immediate, Short-Term, Long-Term) to guide remediation efforts.
Appendices and Supporting Documentation
This final section includes any supplementary materials that provide further detail or evidence for the findings presented in the main body. This might include detailed log excerpts, network diagrams, physical security schematics, configuration files, interview transcripts, vulnerability scan reports, or other relevant technical documentation. These appendices offer robust support for the audit’s conclusions.
Best Practices for Utilizing a Data Center Audit Report Template
Leveraging a Data Center Audit Report Template effectively goes beyond simply filling in the blanks; it involves a strategic approach to continuous improvement and risk management. Adhering to best practices ensures that the audit process delivers maximum value and contributes to the overall resilience and efficiency of the data center.
Firstly, regularity and consistency are paramount. Audits should not be one-off events but rather part of a scheduled, recurring cycle. Whether quarterly, semi-annually, or annually, establishing a consistent audit cadence allows for continuous monitoring of the data center’s health and tracking of progress on previously identified issues. Using the same template consistently across these audits enables easy comparison of results over time, highlighting trends and the effectiveness of remediation efforts.
Secondly, foster cross-functional team involvement. A comprehensive data center audit requires expertise from various domains, including IT operations, network engineering, physical security, compliance, and management. Involving key stakeholders from each area in the audit process – from planning to review – ensures that all relevant perspectives are considered and that the audit findings are accurate and well-rounded. Their input is also crucial for developing practical and effective recommendations.
Furthermore, it’s vital to prioritize and action findings diligently. An audit report is only as valuable as the actions it inspires. Upon completion, the report should be reviewed by all relevant stakeholders, and a clear action plan must be developed based on the recommendations. Issues should be prioritized based on their severity and potential business impact. Assigning clear ownership and realistic deadlines for each action item ensures accountability and progress. Regular follow-up meetings should be scheduled to track the implementation of recommendations and address any roadblocks.
Finally, integrate audit findings into a continuous improvement cycle. The audit should not be seen as an endpoint but as a catalyst for ongoing enhancement. Lessons learned from each audit should feed back into operational procedures, policy updates, and future planning. This continuous feedback loop helps refine the data center’s security posture, optimize its performance, and maintain compliance in an ever-evolving technological landscape. By treating the audit report as a living document that drives strategic initiatives, organizations can ensure their data centers remain robust and resilient.
Customizing Your Data Center Audit Report Template for Specific Needs
While a standard Data Center Audit Report Template provides an excellent foundation, its true power often lies in its adaptability. No two data centers are exactly alike, and their specific operational contexts, regulatory obligations, and business objectives necessitate a degree of customization in the audit reporting process. Tailoring your template ensures that the audit directly addresses the most critical concerns relevant to your organization.
One of the primary drivers for customization is industry-specific regulatory compliance. For instance, a healthcare organization must ensure its data center audit report explicitly addresses HIPAA compliance, detailing how patient data is protected, transmitted, and stored according to strict regulations. Similarly, financial institutions will need sections dedicated to PCI DSS requirements for cardholder data or Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX) compliance for financial reporting. Government agencies might adhere to NIST frameworks, while European businesses must consider GDPR. Customizing the template to include specific sections, checklists, or references to these regulations makes the audit report a powerful compliance tool.
Another key aspect of customization relates to the scale and complexity of the data center. A small server room with a handful of racks will have different audit priorities than a hyperscale facility spanning multiple buildings. For smaller operations, the template might streamline certain sections, focusing on core infrastructure and basic security. For larger, distributed environments, the template may need expanded sections on network segmentation, advanced virtualization, multi-site redundancy, and more complex operational governance. Adding fields for specific equipment models, rack locations, or detailed power usage effectiveness (PUE) metrics can also be beneficial.
Furthermore, customization can reflect internal organizational priorities and risk appetite. If a company prioritizes energy efficiency, the template could include more detailed sections on PUE analysis, cooling system performance metrics, and energy-saving initiatives. If disaster recovery is a major concern, the template might expand on recovery point objectives (RPOs), recovery time objectives (RTOs), and detailed testing scenarios. Integrating sections that align with specific internal security policies or incident management protocols ensures that the audit directly supports the organization’s unique operational philosophy. By thoughtfully adapting the template, organizations can create an audit report that is not just comprehensive, but also highly relevant and maximally impactful for their distinct environment.
Conclusion
The integrity and efficiency of a data center are paramount to modern business success, and at the heart of maintaining these critical assets lies the systematic rigor of a well-executed audit. A robust Data Center Audit Report Template is an indispensable tool in this process, providing the structure and consistency needed to transform complex technical assessments into clear, actionable insights. From detailing physical security vulnerabilities to dissecting logical network configurations and assessing regulatory compliance, a comprehensive template ensures that no critical aspect is overlooked.
By utilizing a standardized template, organizations can streamline their audit processes, facilitate better communication among stakeholders, and track progress on identified issues over time. It empowers businesses to proactively manage risks, enhance operational efficiency, and demonstrate due diligence to regulatory bodies and clients. Ultimately, a customized and diligently applied data center audit report template serves as a vital blueprint for continuous improvement, securing the foundational infrastructure that powers today’s digital world and ensuring sustained business resilience.
]]>